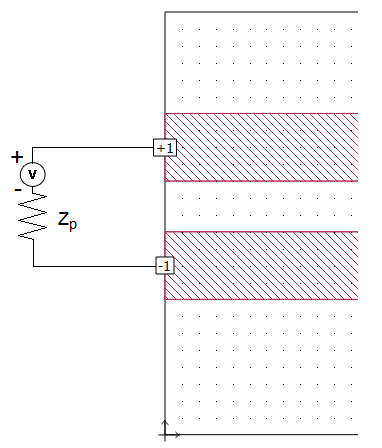
To model differential mode in Sonnet, two ports using the same port number, one positive and one negative, should be used. Em sums the total current going into all the positive ports with the same port number and sets that equal to the total current going out of all the ports with that same negative port number. For example, for a circuit with a +1 port and a -1 port, em sets current flowing into port +1 to be equal to the current flowing out of port -1. These are differential mode ports (sometimes called “balanced”, “push-pull” or “odd-mode” ports). An example is shown below. Zp is the impedance of the port.