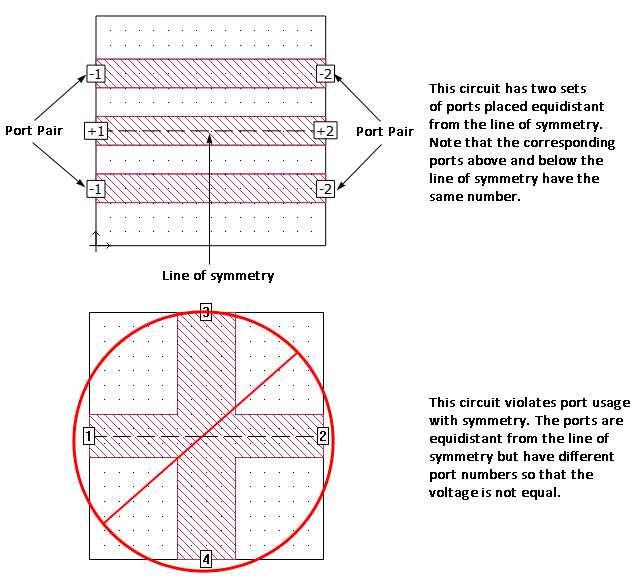
Symmetry can be used to considerably reduce the amount of memory and processing time required to analyze a circuit which is symmetrical about the midline of the substrate. When symmetry is turned on in the Box page of the Circuit Settings dialog box , everything below the line of symmetry is ignored, and all metal above the line of symmetry is “reflected” about the symmetry line. Special care should be given to ports when using symmetry.
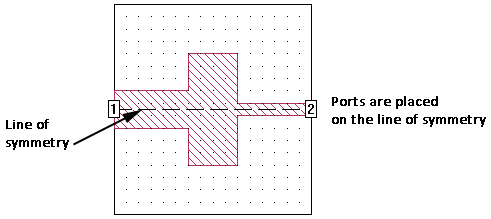
Normally, if you are using symmetry, ports are placed on the line of symmetry as pictured below.
Ports can be placed off the line of symmetry, but the port placed above the line of symmetry must have another port equidistant from and below the line of symmetry. These two ports must also have the same port type, port number and properties. The basic premise of symmetry is that the voltage at any given point above the line of symmetry must be equal to the voltage at the corresponding location below the line of symmetry. Using the same port number, port type and properties ensures that the voltage is the same at both required points since all ports with the same number, as pictured below, are electrically connected together.